Interactive online versions:
Validation of Spin-Flip scattering with gepore.f (field in-plane)¶
This example demonstrates the use of the gepore_zeeman.f program (a modification of the original gepore.f published in the PNR book chapter [1]) to validate a model with
strong spin-flip scattering
moderate magnetic field
field \(\vec H\) in the sample plane
magnetization \(\vec M\) in the sample plane, but slightly (20 degrees) rotated from \(\vec H\)
[1] Majkrzak, C., O’Donovan, K. & Berk, N. (2006). Neutron Scattering from Magnetic Materials, edited by T. Chatterji, pp. 397–471. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science.
[1]:
# Install refl1d if it is not already installed
try:
import refl1d
except ImportError:
%pip install -q "refl1d @ git+https://github.com/reflectometry/refl1d"
import refl1d
[2]:
import numpy as np
from refl1d.validation.gepore_runner import GeporeRunner
# start a GeporeRunner instance
runner = GeporeRunner()
QS = 0.001 # start value of Q
DQ = 0.0004 # step size in Q
NQ = 80 # number of Q points
Qz = np.arange(NQ) * DQ + QS
Define the sample as a list of layers:
(note that the magnetic layer is rotated 20 degrees wrt. the field)
label |
thickness (A) |
\(\text{SLD}_N\) \((10^{-6}A)\) |
\(\text{SLD}_M\) \((10^{-6}A)\) |
\(\theta_{M}\) \((\text{degrees})\) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
vacuum |
0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
270 |
mag. layer |
1000 |
8.0 |
2.0 |
250 |
cap layer |
500 |
5.0 |
0.0 |
270 |
substrate |
0 |
2.0 |
0.0 |
270 |
[3]:
Aguide = 270.0 # guide field in sample plane
layers = [
# depth rho rhoM thetaM phiM
[0, 0.0, 0.0, 270, 0],
[1000, 8.0, 2.0, 250, 0.0],
[500, 5.0, 0.0, 270, 0.0],
[0, 2.0, 0.0, 270, 0.0],
]
depth, rhoN, rhoM, thetaM, phiM = list(zip(*layers))
applied field, in Tesla, shouldn’t matter for this calculation
[4]:
H = 0.5
Calculating with gepore.f¶
The reflectivities are returned from gepore.f in the order \((r_g^{++}, r_g^{+-}, r_g^{-+}, r_g^{--})\)
NOTE we use a value of \(\text{EPS} = -\text{Aguide}\)
[5]:
EPS = -Aguide
rg = runner.run(layers, QS, DQ, NQ, EPS, H, zeeman_corrections=False)
Rg = [np.abs(r) ** 2 for r in rg]
Calculating with the modified gepore_zeeman.f¶
A version of the original gepore.f that includes Zeeman energy corrections
[6]:
rgz = runner.run(layers, QS, DQ, NQ, EPS, H, zeeman_corrections=True)
Rgz = [np.abs(r) ** 2 for r in rgz]
Calculating reflectivity using Refl1D¶
magnetic_amplitude returns cross-sections in order \((r_1^{--}, r_1^{-+}, r_1^{+-}, r_1^{++})\), so we need to reverse them here to compare to gepore outputs
[7]:
from refl1d.sample.reflectivity import magnetic_amplitude, reflectivity_amplitude
r1 = magnetic_amplitude(Qz / 2, depth, rhoN, 0, rhoM, thetaM, 0, Aguide, H)
R1 = np.abs(r1[::-1]) ** 2
Plots¶
[8]:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
Refl1D vs gepore_zeeman.f¶
[9]:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
xs_labels = ["++", "+-", "-+", "--"]
for i, label in enumerate(xs_labels):
ax.semilogy(Qz, Rgz[i], label=f"gepore_z {label}")
ax.set_prop_cycle(None)
for i, label in enumerate(xs_labels):
ax.semilogy(Qz, R1[i], "o", label=f"refl1d {label}", fillstyle="none")
ax.set_ylabel("Reflectivity")
ax.set_xlabel("2*kz_in")
ax.set_title("Reflectivity with gepore_zeeman.f and Refl1D")
ax.legend()
[9]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f92f75d4650>
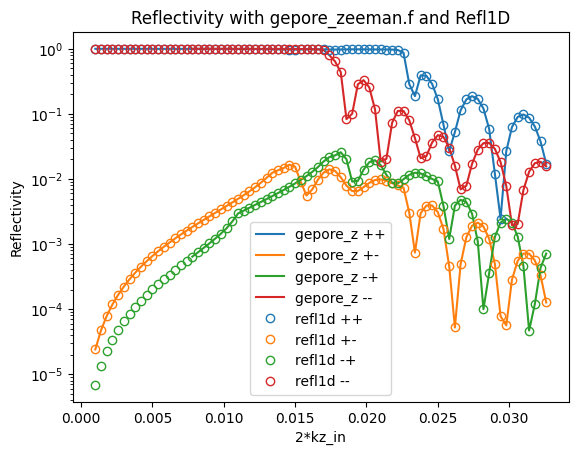
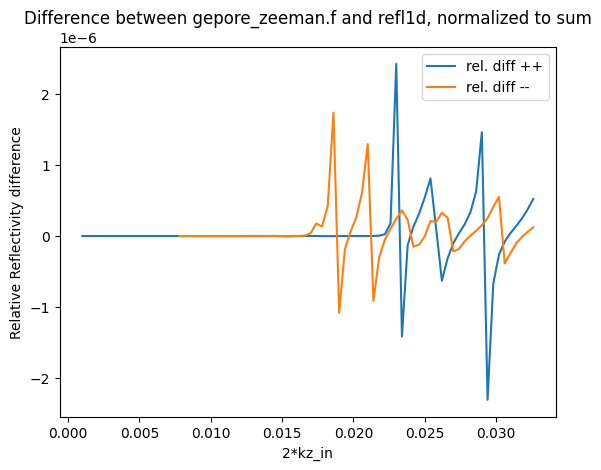
The differences between the two reflectivity outputs are small, and are likely due to differences in the numerical implementation of the reflectivity calculation. Here is a plot of the differences:
[10]:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
xs_labels = ["++", "+-", "-+", "--"]
for i, label in enumerate(xs_labels):
if not i == 1 and not i == 2: # skip +- and -+
ax.plot(Qz, 2 * (Rgz[i] - R1[i]) / np.abs(Rgz[i] + R1[i]), label=f"rel. diff {label}")
ax.set_ylabel("Relative Reflectivity difference")
ax.set_xlabel("2*kz_in")
ax.set_title("Difference between gepore_zeeman.f and refl1d, normalized to sum")
ax.legend()
[10]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f92f523e180>
Refl1D vs gepore.f¶
[11]:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
xs_labels = ["++", "+-", "-+", "--"]
for i, label in enumerate(xs_labels):
ax.semilogy(Qz, Rg[i], label=f"gepore {label}")
ax.set_prop_cycle(None)
for i, label in enumerate(xs_labels):
ax.semilogy(Qz, R1[i], "o", label=f"refl1d {label}", fillstyle="none")
ax.set_ylabel("Reflectivity")
ax.set_xlabel("2*kz_in")
ax.set_title("Reflectivity with gepore.f and Refl1D")
ax.legend()
[11]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f92f505ec00>
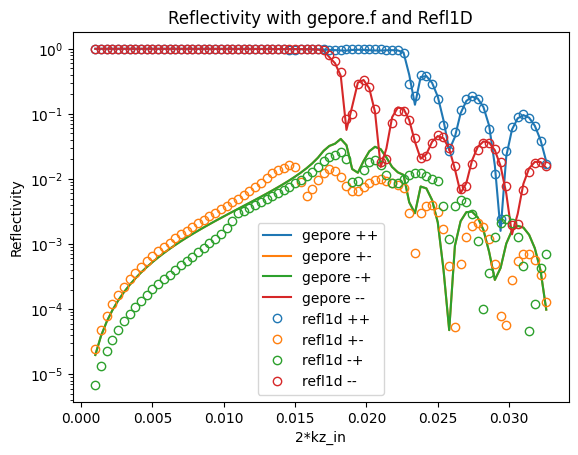
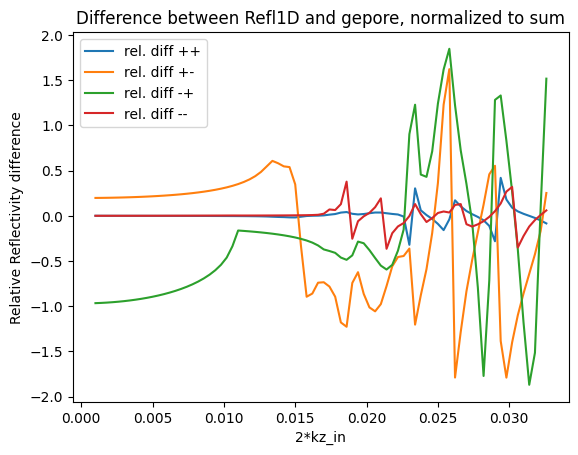
Here the differences are much larger, due to the fact that we are not applying zeeman energy corrections in gepore.f
[12]:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
for i, label in enumerate(xs_labels):
# if not i == 1 and not i == 2: # skip +- and -+
ax.plot(Qz, 2 * (R1[i] - Rg[i]) / np.abs(R1[i] + Rg[i]), label=f"rel. diff {label}")
ax.set_ylabel("Relative Reflectivity difference")
ax.set_xlabel("2*kz_in")
ax.set_title("Difference between Refl1D and gepore, normalized to sum")
ax.legend()
[12]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f92ef7b9550>
[ ]: